
The AV node serves an important function as a "gatekeeper", limiting the electrical activity that reaches the ventricles. After a brief delay at the AV node, the stimulus travels through the bundle of His to the left and right bundle branches and then to the Purkinje fibers and the endocardium at the apex of the heart, then finally to the ventricular myocardium. From there, the electrical stimulus is transmitted via internodal pathways to the atrioventricular (AV) node. Transmission of a cardiac action potential through the conduction system of the normal human heartĮlectrical activity in the normal human heart begins when a cardiac action potential arises in the sinoatrial (SA) node, which is located in the right atrium. The condition is named after Louis Wolff, John Parkinson, and Paul Dudley White who described the ECG findings in 1930. In those with WPW complicated by atrial fibrillation, cardioversion or the medication procainamide may be used. In those without symptoms ongoing observation may be reasonable. In some cases, non-invasive monitoring may help to more carefully risk stratify patients into a lower risk category. The risk of death in those without symptoms is about 0.5% per year in children and 0.1% per year in adults. It affects between 0.1 and 0.3% in the population. WPW syndrome may be monitored or treated with either medications or an ablation (destroying the tissues) such as with radiofrequency catheter ablation. The diagnosis of WPW occurs with a combination of palpitations and when an electrocardiogram (ECG) show a short PR interval and a delta wave. It is associated with other conditions such as Ebstein anomaly and hypokalemic periodic paralysis. The underlying mechanism involves an accessory electrical conduction pathway between the atria and the ventricles. A small number of cases are due to a mutation of the PRKAG2 gene which may be inherited from a person's parents in an autosomal dominant fashion. The cause of WPW is typically unknown and is likely due to a combination of chance and genetic factors. The most common type of irregular heartbeat that occurs is known as paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia. About 60% of people with the electrical problem developed symptoms, which may include an abnormally fast heartbeat, palpitations, shortness of breath, lightheadedness, or syncope. Wolff–Parkinson–White syndrome ( WPWS) is a disorder due to a specific type of problem with the electrical system of the heart.
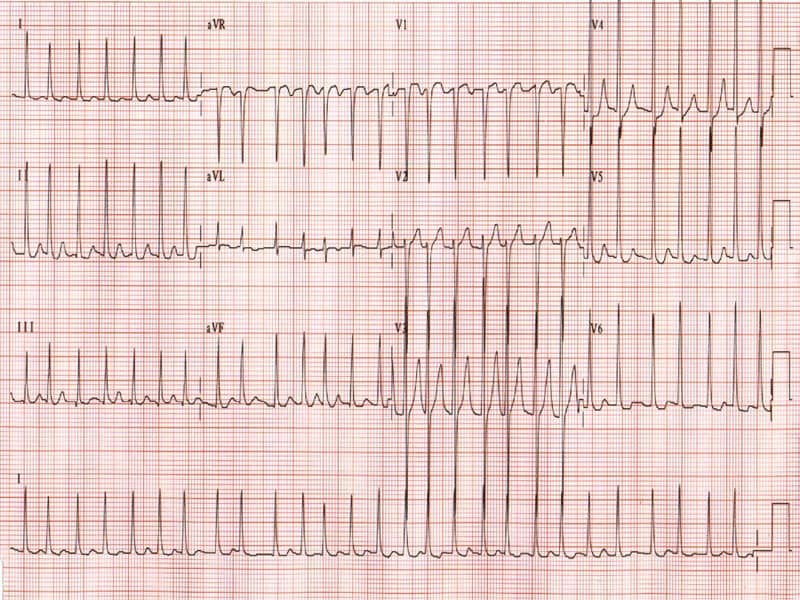
Without symptoms 0.5% (children), 0.1% (adults) risk of death per year Watchful waiting, medications, radiofrequency catheter ablation Note the short PR interval.Ībnormally fast heartbeat, palpitations, shortness of breath, lightheadedness, loss of consciousness Ĭardiomyopathy, stroke, sudden cardiac death Įlectrocardiogram shows a short PR interval and a wide QRS complex from a delta wave WPW pattern, Ventricular pre-excitation with arrhythmia, auriculoventricular accessory pathway syndrome Ĭonduction through the accessory pathway results in a delta wave.Ī characteristic "delta wave" (arrow) seen in a person with Wolff–Parkinson–White syndrome. Medical condition Wolff–Parkinson–White syndrome


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
